Production- Camera Setup
- Pixel Aspect Ratio- 720/1080/4k- figure relates to how many pixels the image is; more pixels, better the quality. Settings > video settings > resolutions >alter.
- Frame rates-24fps (main)/30fps/50fps/50fps/60fps (frames per second)
- ISO (native ISO/ below 640)
- Shutter speed-1/50 for decent light or 1/25 for low light. – double your frame rate
- Card Format- delete all data and sync card and camera.
Production- Shot Reverse- Shot
180-degree rule

- The 180-degree rule helps the audience interpret where characters are in a scene without seeing the full set. If you want to disorientate your audience, break the 180-degree rule, however if the rule were to be broken without the proper intent, it would just confuse the audience and the scene would not come together properly.
Production- Lighting the scene.
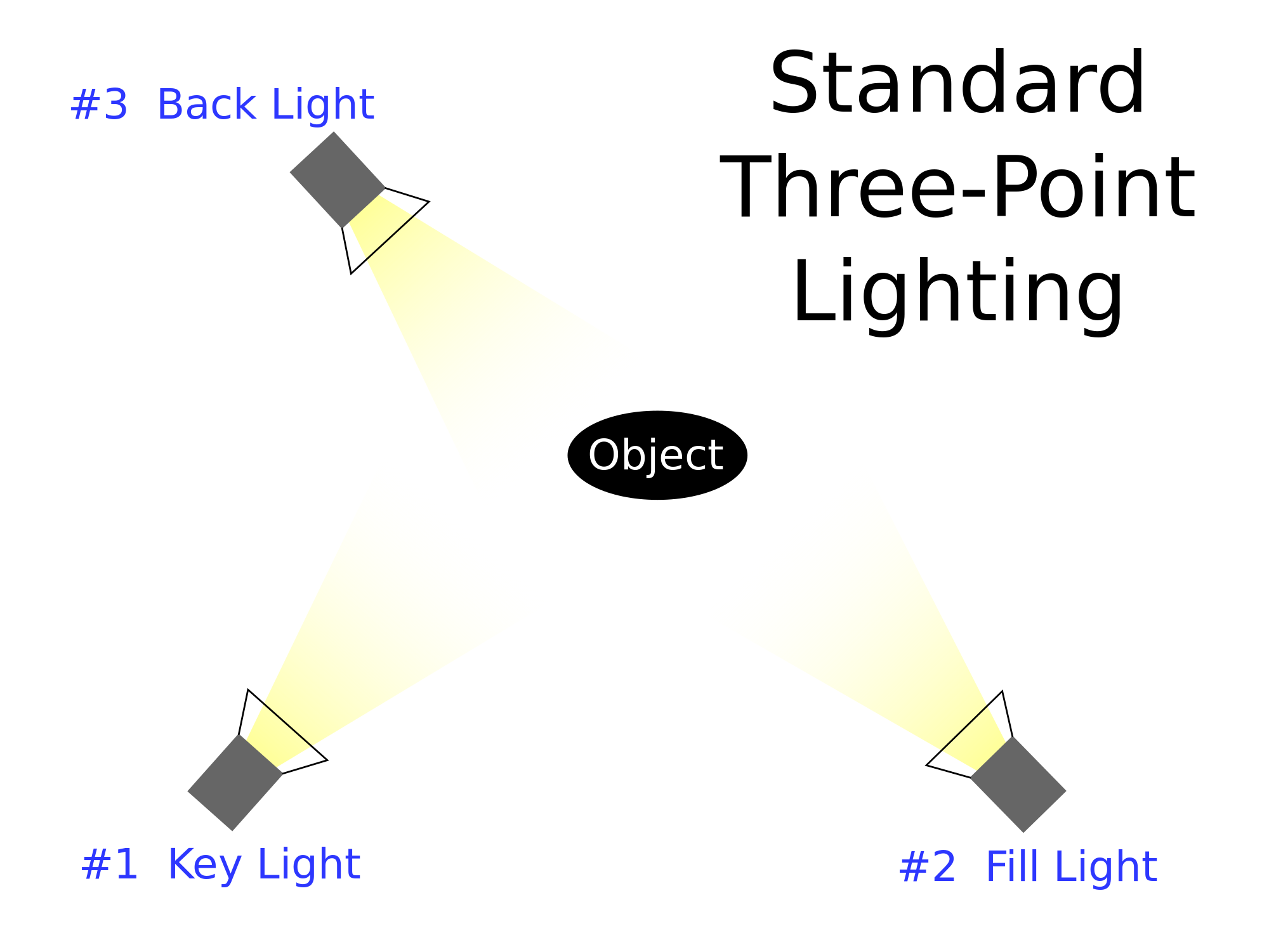
Three-point lighting uses a back light, a key light and a fill light. Of course the lighting can be changed if the scene is intended to be darker or lighter, but to light the whole subject, this is how it would be done.
Post-production- Setting a project up- When setting a project up the save location should be secure and sizeable, the scratch disks and media cache has to be saved to the same location. In post-production, it has to be ensured that the sequence to match the camera/footage settings. Lastly, the work space windows have to be set up accordingly.
Stages of editing
- Footage assembly and refining sequence.
- Building a soundtrack
- Titles and graphics
- Special and visual effects
- Colour correction and grading
- Extras (vignette, overlays and presets, LUTS etc.)